Exploring the Benefits of Magnesium for Health and Wellness

Magnesium is one of the most important minerals in the human body, yet it is often overlooked compared to vitamins and other nutrients. It plays a critical role in more than 300 biochemical reactions, influencing everything from muscle function to heart health. Despite its importance, many people worldwide do not consume enough magnesium, leading to deficiencies that can affect overall well-being. This article takes an in-depth look at magnesium, its benefits, sources, and why it should be considered an essential part of a healthy lifestyle.
A Closer Look at Magnesium: Expert Insights
For individuals seeking detailed information, exploring a magnesium review can provide valuable insights into how this mineral impacts energy, mood, sleep, and overall health. Such reviews often highlight the scientific evidence behind magnesium’s role, making it easier to understand its benefits and the potential consequences of deficiency.
Why Magnesium Is Essential
Magnesium is a vital mineral that supports numerous functions in the body. Some of its key roles include:
- Energy production: It helps convert food into energy at the cellular level.
- Muscle function: Magnesium regulates muscle contractions and helps prevent cramps.
- Nervous system support: It balances neurotransmitters, aiding relaxation and mood stability.
- Bone health: Magnesium works alongside calcium and vitamin D to maintain strong bones.
- Heart function: It contributes to normal heart rhythms and blood pressure regulation.
Because of its wide-ranging influence, magnesium deficiency can manifest in many different ways, from fatigue and irritability to muscle weakness and irregular heartbeat.
The Connection Between Magnesium and Stress
Modern lifestyles often expose people to chronic stress, and magnesium plays an important role in how the body responds. It helps regulate cortisol, the stress hormone, and supports relaxation by influencing neurotransmitters such as GABA. People with low magnesium levels may find it harder to manage stress, which can create a cycle of tension, poor sleep, and fatigue.
Ensuring sufficient magnesium intake can improve resilience against stress and contribute to a calmer, more balanced state of mind.
Magnesium and Sleep Quality
One of the most recognized benefits of magnesium is its impact on sleep. Magnesium supports the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. It also promotes muscle relaxation, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep through the night.
Studies suggest that people with low magnesium levels are more likely to experience insomnia and restless nights. Increasing intake through diet or supplementation may help improve sleep quality naturally.
Heart Health and Magnesium
Magnesium is also essential for cardiovascular health. It helps regulate blood pressure, supports healthy cholesterol levels, and contributes to overall circulation. Some research suggests that magnesium may lower the risk of heart disease by reducing arterial stiffness and preventing calcium buildup in the arteries.
Maintaining proper magnesium levels can therefore be a protective factor for long-term heart health, especially for individuals with high blood pressure or other cardiovascular risks.
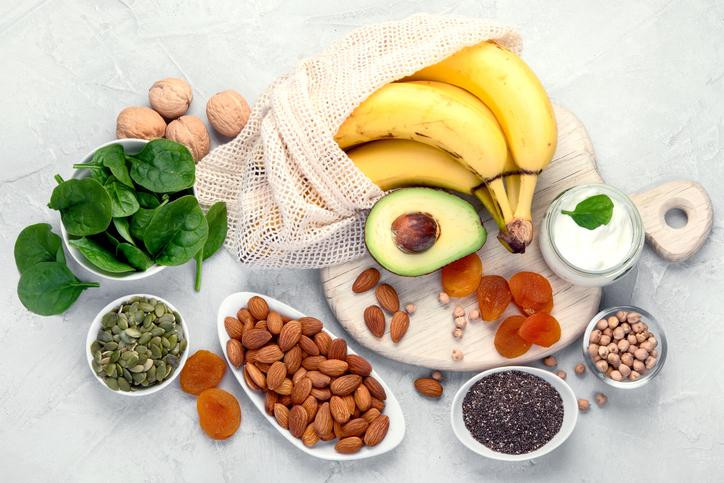
Food Sources of Magnesium
Fortunately, magnesium is found in a wide range of foods, making it possible to meet daily needs with a balanced diet. Some of the best natural sources include:
- Leafy green vegetables such as spinach and kale
- Nuts and seeds like almonds, cashews, and pumpkin seeds
- Whole grains such as brown rice and oats
- Legumes, including beans, lentils, and chickpeas
- Dark chocolate (in moderation)
Despite the availability of magnesium-rich foods, many people still fail to meet recommended intake levels, often due to processed diets that lack whole, nutrient-dense options.
Who Is at Risk of Magnesium Deficiency?
Several groups are more vulnerable to magnesium deficiency:
- Older adults: Absorption decreases with age.
- People with digestive issues: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease affect absorption.
- Individuals with type 2 diabetes: High blood sugar can increase magnesium loss through urine.
- People who consume excessive alcohol: Alcohol interferes with magnesium balance in the body.
Symptoms of deficiency may include fatigue, irritability, headaches, muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat, and even mood disorders. Recognizing these signs early is essential for prevention.
Safe Intake and Supplementation
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for magnesium varies by age and gender but generally ranges between 300–420 mg per day for adults. While it is best to obtain magnesium from natural food sources, supplementation is often considered for people who struggle to meet their needs through diet alone.
Supplements come in various forms, such as magnesium citrate, magnesium glycinate, and magnesium oxide. Some are better absorbed than others, and the choice may depend on individual needs. For example, magnesium glycinate is often recommended for improving sleep and relaxation, while magnesium citrate is commonly used to support digestion.
Although magnesium supplements are generally safe, excessive intake can lead to digestive discomfort, including diarrhea. Consulting with a healthcare professional before starting supplementation ensures proper dosage and safety.
Long-Term Benefits of Magnesium
Maintaining adequate magnesium levels provides several long-term health benefits, including:
- Stronger bones and reduced risk of osteoporosis
- Better stress management and improved mental health
- Reduced risk of high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease
- Improved sleep and energy balance
- Enhanced muscle performance and recovery
These wide-ranging benefits show why magnesium is often referred to as a “master mineral.”
Final Thoughts
Magnesium may not always be in the spotlight, but its influence on health is undeniable. From supporting sleep and reducing stress to promoting strong bones and a healthy heart, this essential mineral plays a foundational role in everyday wellness.
By eating a magnesium-rich diet and considering supplementation when necessary, individuals can protect themselves against deficiency and enjoy the wide-ranging benefits of this powerful nutrient. Maintaining healthy magnesium levels is a simple yet effective step toward long-term vitality and balance.