Mastering Heavy Bolting: A Complete Insight into Hydraulic Torque Technology
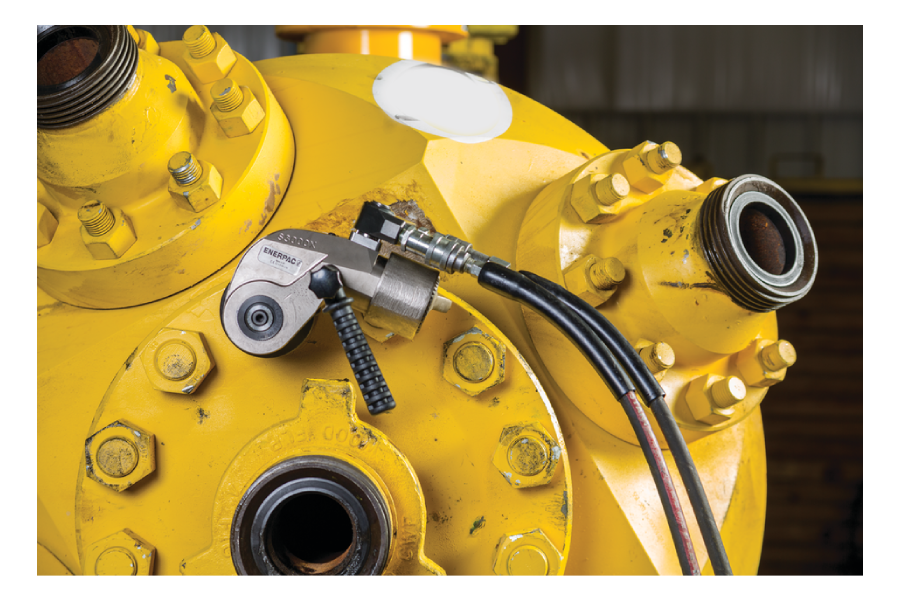
In large-scale industrial environments, fastening is far more than a simple mechanical task. It directly affects safety, structural integrity, and operational reliability. Industries such as oil and gas, power generation, petrochemicals, construction, and heavy manufacturing deal with high-load joints that must withstand vibration, pressure, and extreme temperatures. In such conditions, traditional manual or pneumatic tools often fail to deliver the required accuracy and consistency.
A hydraulic torque wrench plays a vital role in these demanding applications by delivering controlled and repeatable torque output for critical bolting operations. This advanced tool has become a standard solution wherever high-torque precision is required, ensuring bolts are tightened exactly to specification without compromising safety or efficiency.
Understanding Hydraulic Torque Systems
Hydraulic torque systems function by converting hydraulic pressure into rotational force. A powered pump generates pressure that travels through reinforced hoses to the wrench head, where it is transformed into torque. This method allows operators to achieve extremely high torque values with minimal physical effort.
Unlike impact tools, which rely on sudden bursts of force, hydraulic torque systems apply smooth and steady pressure. This controlled action significantly reduces the risk of over-tightening, bolt damage, or uneven load distribution. As a result, joints remain secure and reliable over long operational periods.
Core Components and How They Work Together
A hydraulic torque setup consists of several precisely engineered components:
- Hydraulic Pump: Supplies pressurized fluid and controls torque output. Pumps may be electric, pneumatic, manual, or battery-powered depending on job site requirements.
- Torque Wrench Assembly: The mechanical unit that applies torque to the fastener.
- High-Pressure Hoses: Transfer hydraulic fluid safely and efficiently.
- Reaction Mechanism: Absorbs counterforce to stabilize the tool during operation.
Each component is designed to withstand high pressure and harsh working environments, ensuring dependable performance even under continuous use.
Types of Hydraulic Torque Wrenches
Different industrial scenarios require different wrench designs. The most common types include:
Square Drive Torque Wrenches
These are widely used due to their flexibility. They accept interchangeable sockets, making them suitable for a wide range of bolt sizes and applications.
Low-Profile Torque Wrenches
Designed for restricted spaces, these tools are ideal for flange connections and compact assemblies where clearance is limited.
Specialized Torque Systems
Some applications require customized solutions, such as subsea or hazardous-area-rated tools, built to meet specific environmental and safety standards.
Selecting the correct type ensures efficiency, accuracy, and operator safety.
Industrial Applications and Use Cases
Hydraulic torque technology is trusted across multiple sectors:
- Oil and Gas: Securing pipeline flanges, pressure vessels, and offshore platform components.
- Power Plants: Turbines, generators, and boiler assemblies rely on precise bolting.
- Wind Energy: Tower sections, nacelles, and blade connections demand uniform torque.
- Construction and Infrastructure: Bridges, steel structures, and heavy machinery depend on secure fastening.
- Mining and Marine: Equipment exposed to vibration and harsh conditions requires reliable torque control.
In each of these industries, accurate bolting prevents leaks, structural failure, and costly downtime.
Advantages Over Conventional Bolting Methods
Hydraulic torque solutions offer several significant benefits:
- Exceptional Accuracy: Ensures compliance with engineering torque specifications.
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces manual strain and minimizes the risk of tool slippage.
- Operational Efficiency: Faster tightening cycles compared to manual methods.
- Consistency: Uniform torque across multiple fasteners improves joint reliability.
- Durability: Built for long-term use in extreme industrial environments.
These advantages make hydraulic torque tools a cost-effective investment for organizations focused on quality and safety.
Safety Guidelines and Best Practices
Although hydraulic torque systems are designed for safety, proper use is essential. Operators should always follow these best practices:
- Verify torque values before beginning any operation.
- Inspect hoses, couplings, and seals for wear or damage.
- Position the reaction arm securely against a solid surface.
- Use calibrated equipment to maintain torque accuracy.
- Follow manufacturer instructions for operation and maintenance.
Regular training ensures that operators understand both the capabilities and limitations of the equipment.
Maintenance, Calibration, and Longevity
Routine maintenance is critical for preserving performance. Hydraulic fluid should be checked and replaced as recommended, and seals should be inspected regularly. Calibration ensures that torque output remains accurate over time, which is especially important in regulated industries.
Preventive maintenance not only extends tool life but also protects expensive equipment and infrastructure by ensuring fasteners are tightened correctly every time.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Hydraulic Torque Solution
Before selecting a system, it’s important to evaluate:
- Required torque range
- Available working space
- Frequency of use
- Environmental conditions
- Power source availability
Partnering with a reliable supplier that provides technical guidance, after-sales support, and calibration services can greatly enhance long-term value.
Future Trends in Hydraulic Torque Technology
As industries evolve, so does torque technology. Modern developments include lightweight materials, digital torque monitoring, and smart pumps that record torque data for quality assurance. Battery-powered systems are also gaining popularity, offering portability without sacrificing performance.
These innovations are helping organizations meet stricter safety regulations while improving productivity and operational transparency.
Conclusion
Precision bolting is a cornerstone of industrial safety and performance. Hydraulic torque solutions provide the accuracy, consistency, and reliability required for critical applications across multiple industries. By understanding how these systems work and following best practices, professionals can ensure secure fastening, reduced downtime, and long-term operational success.
In a world where even a single improperly tightened bolt can lead to major failures, investing in advanced torque technology is not just a choice—it’s a necessity.






