The Role of Bioassay Testing in Aquatic Environments

Introduction
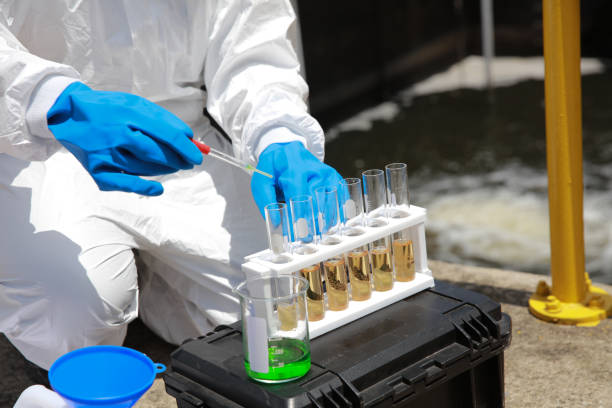
Bioassay testing is a vital method for evaluating the effects of various substances on aquatic life. This type of testing helps ensure the health and sustainability of aquatic ecosystems by analyzing the toxicity and biological impact of chemicals, pollutants, and other potential hazards. This article explores the principles, methodologies, and importance of bioassay testing in aquatic environments.
What is Aquatic Bioassay Testing?
Aquatic bioassay testing involves using living aquatic organisms to assess the toxicity, concentration, and biological effects of substances in water. Organisms commonly used in these tests include fish, invertebrates, algae, and microorganisms. By observing the responses of these organisms, scientists can infer the potential impact of contaminants on aquatic ecosystems.
Key Methodologies in Aquatic Bioassay Testing
- Static Tests: In static bioassays, organisms are exposed to a test substance in a controlled environment without changing the test medium. This method is straightforward and cost-effective but may not accurately reflect natural conditions where water flow and pollutant dilution occur.
- Flow-through Tests: These tests involve a continuous flow of water through the test chambers, simulating more realistic conditions of natural water bodies. This approach helps maintain consistent exposure levels and reduces waste buildup, providing a clearer picture of long-term effects.
- Renewal Tests: Renewal bioassays periodically replace the test medium with fresh solution, maintaining stable conditions for the test organisms. This method combines the advantages of static and flow-through tests by providing controlled exposure while mitigating waste accumulation.
- Toxicity Identification and Evaluation (TIE): TIE procedures are designed to identify specific toxicants responsible for observed effects. By fractionating and manipulating test samples, researchers can pinpoint the substances causing toxicity and develop targeted mitigation strategies.
Importance of Aquatic Bioassay Testing
- Environmental Protection: Aquatic bioassay testing is essential for protecting aquatic ecosystems from harmful pollutants. By identifying toxic substances and their concentrations, regulators can implement measures to prevent contamination and preserve water quality.
- Regulatory Compliance: Governments and environmental agencies mandate aquatic bioassay testing to ensure industries comply with environmental regulations. These tests are critical for approving new chemicals, assessing wastewater discharges, and monitoring environmental remediation efforts.
- Risk Assessment: Bioassays provide valuable data for ecological risk assessments, helping predict the potential impact of pollutants on aquatic life. This information guides decision-making processes for environmental management and conservation.
- Public Health: Since water bodies are often sources of drinking water and recreation, ensuring their safety is vital for public health. Aquatic bioassay testing helps prevent human exposure to hazardous substances through contaminated water.
Applications of Aquatic Bioassay Testing
- Industrial Discharges: Industries use aquatic bioassays to test the toxicity of their effluents before releasing them into water bodies. This process helps identify harmful substances and ensures discharge limits are not exceeded.
- Pesticide Evaluation: Pesticides can have unintended effects on non-target aquatic organisms. Bioassay tests assess the environmental impact of these chemicals, guiding safe application practices and regulatory standards.
- Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products: Many pharmaceuticals and personal care products end up in water systems, potentially affecting aquatic life. Bioassay testing helps understand the ecological impact of these substances and informs regulations to limit their presence in the environment.
- Environmental Monitoring: Regular bioassay testing is conducted as part of environmental monitoring programs to detect changes in water quality over time. This ongoing assessment helps identify pollution sources early and implement corrective measures.
Conclusion
Aquatic bioassay testing is a crucial tool in environmental science, providing essential insights into the impact of various substances on aquatic ecosystems. Through meticulous testing and analysis, it ensures the protection of water bodies, compliance with environmental regulations, and the safeguarding of public health. As our understanding of aquatic ecosystems evolves, the role of bioassay testing in preserving the delicate balance of these environments becomes increasingly important.